Aero-Optics
As a planar optical wavefront propagates through a fluid medium with varying index-of-refraction, such as turbulent shear layers and atmospheric boundary layers, the wavefront becomes distorted (some parts advance farther than others). For airborne laser systems, the aberrating flow field is conventionally divided into two regimes.
The first regime is the aperture's near field where the optical aberration arises from unsteady flow structures. The optical distortion in this regime is termed "aero-optics problem". For example, laser communication devices mounted on high speed airborne aircraft can induce sparated turbulent flows around the aperture, and these flows degrade the beam's ability to focus in the far field.
The second regime is the Earth's atmosphere, which affects the long-range propagation of a laser beam. Optical distortions in this regime are referred to as "atmospheric propagation problem". They usually involve very large flow structures at very low frequencies, and can be corrected by static optical components or adaptive optical (AO) systems.
Aberrations in the first regime are of high frequency and are difficult to correct. In the early days of laser technology, the aero-optical aberrations were of small magnitude ( 1m) compared with the long optical wavelength ( 10m) and are found to be unimportant. However, since the 80's, breakthroughs have been made in laser technology, and lasers with much shorter wavelengths ( 1m) become popular. For this reason, the increased relative optical aberrations has become a serious problem.
Optical aberrations originate from variations of the refractive index that is directly related to air density through the Gladstone-Dale relation, where is the refractive index, and is the Gladstone-Dale constant. For light with wavelengths between 1m and 10m traveling in the air at standard condition (Pa, K, ), is approximately . The nondimensional form of the Gladstone-Dale relation is where is the nondimensional Gladstone-Dale constant, is the reference density, and is the nondimensional density. If the standard atmospheric density is taken as the reference value, the nondimensional Gladstone-Dale constant is .
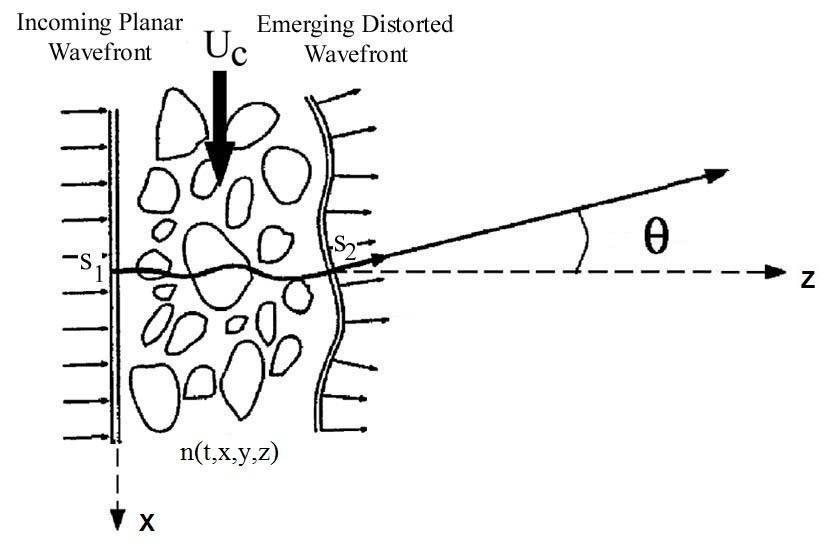
A wavefront is a surface with constant phase value, and is equivalent to a surface with constant optical path length (OPL),
where is the beam propagation direction; define the plane of the initial planar wavefront that is perpendicular to the beam direction. Here we have made an assumption that the integration path is short such that there is no noticeable change in the beam direction, i.e., the angle in the figure below is small. This assumption is valid for most aero-optics problems.
In practice, the difference between a distorted wavefront and its spatial mean position is more important than the wavefront itself, and this difference is defined as the optical path difference (OPD),
where the angle bracket means spatial average over the aperture. Conventionally, "OPD" is used interchangeably with "wavefront". This is because that OPD is in fact the conjugate of a wavefront's variation part and has the same characteristics as a wavefront.
The overall effect of aberrations over the whole aperture in the farfield is measured by the Strehl ratio where is the on-axis irradiance and is the diffraction-limited on-axis irradiance. Based on the large aperture approximation (LAA), the Strehl ratio can be estimated as where is the wavelength and is the root mean square of over the aperture. The time-averaged Strehl ratio is used more often to measure the far-field optical quality, which naturally makes one of the most important parameters in aero-optics.
As previously discussed, is the conjugate of a wavefront, thus a wavefront can be written as Performing a Taylor series expansion on the wavefront, one can get where is a constant referred to as steady (or piston) component; and are the instantaneous tip and tilt components, respectively; is the high-order term with small amplitude but high frequency. The steady, tip, and tilt components can be effortlessly corrected using AO systems, but the high-order component cannot be easily corrected, making it the most detrimental to optical systems. It is therefore customary to focus on the high-order wavefront (i.e., with steady, tip, and tilt components removed) in aero-optics study.